
Maintenance
Guide to ensure the smooth operation and maintenance of your anynode system. It covers essential elements crucial for the efficient upkeep of your anynode – The Software SBC installation.
The following is a thorough guide to ensure the smooth operation and maintenance of your system. It covers essential elements crucial for the efficient upkeep of your anynode installation.
The subsections include:
-
Maintenance Mode: This subsection details the procedures for initiating and managing Maintenance Mode, providing insights into temporary service interruptions and system adjustments.
-
Shutdown or Reboot: Here, you'll find instructions on the proper steps to safely shutdown or reboot your anynode system, minimize risks, and maintain data integrity.
-
Monitor settings: This section delves into configuring and managing monitor settings, offering insights into optimizing performance and monitoring key system parameters.
-
Password Reset: If you have forgotten all your administrative passwords for the anynode frontend, it is possible to reset the password and assign a new one. The steps for this process vary depending on the operating system.
-
System settings: When working on a remote system, some settings on the host system are necessary. See what anynode can change out of the user interface.
-
Core Dump Files: In the rare event of a crash, anynode automatically generates core dump files (
.dmpfiles) to assist in troubleshooting and debugging. These files contain valuable diagnostic information about the state of the application at the time of the crash.

Each subsection within the Maintenance chapter equips users with the knowledge and steps necessary to perform routine maintenance tasks effectively, ensuring the reliability and longevity of your anynode deployment.
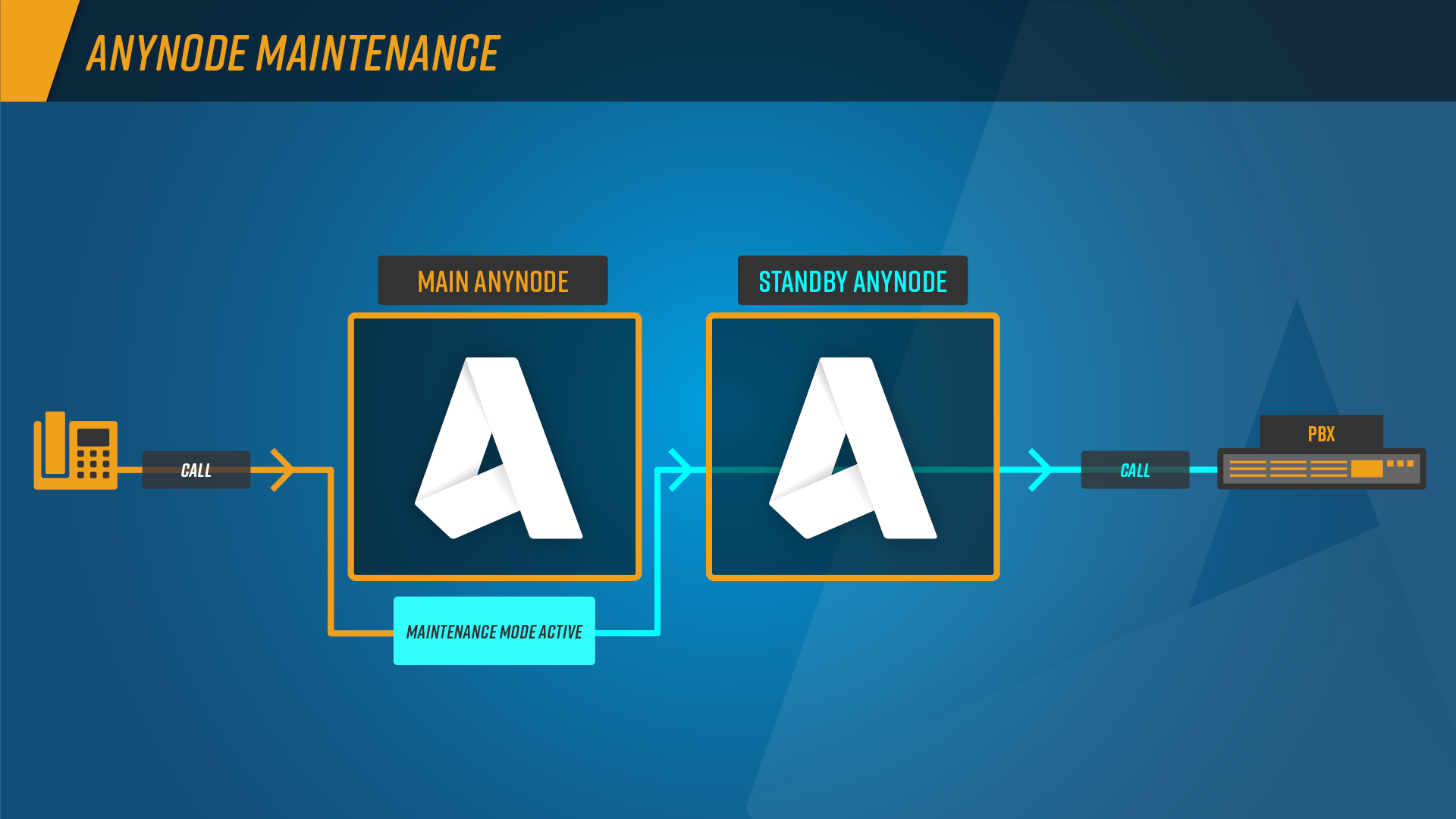
In some situations, you may need to modify the operating system that anynode is running on, which may result in a reboot. To avoid any issues, it is recommended that you enable maintenance mode for anynode before performing any updates or reboots. To comply with all infrastructure endpoints, the maintenance mode offers a various set of options.
Companies must ensure that they can be always reached by phone, in addition to maintaining a smoothly running IT system. To improve reliability and fault tolerance, a second, redundant PBX system and/or access to an alternative provider can be implemented. A fault-tolerant system comprises two anynode installations running on different computers in active or passive mode. The maintenance mode helps to keep the telephony service up and running.
To ensure the long-term stability and optimal performance of your anynode system, consider the following data management practices with the monitor settings:
-
Data Collection Limitation:
anynode allows you to limit the amount of data collected during specific activities. By doing so, you can prevent unnecessary data accumulation, which can impact system efficiency.
Evaluate which data points are essential for your operations and configure anynode accordingly to collect only relevant information.
-
GDPR Compliance and Call Detail Records (CDRs):
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates responsible handling of personal data. For CDRs (containing call-related information), compliance is crucial.
To meet GDPR requirements, set up a retention policy for CDRs. After a specified period, anynode should automatically delete these records to respect individuals’ privacy rights.
-
Call Recording Retention Rules:
Call recordings serve various purposes, including quality assurance and legal compliance. However, retaining them indefinitely is unnecessary and may pose privacy risks.
Define retention rules for call recordings. Determine how long they should be stored based on regulatory guidelines and organizational needs.
-
Event Log Data Management:
Event logs capture system activities, errors, and relevant information. Over time, older log entries may become less relevant.
Regularly review event logs and remove outdated entries. This practice optimizes disk space usage and ensures that only relevant log data is retained.
Remember that effective data management contributes to system reliability, compliance, and efficient resource utilization.