SNMP Queries Using PowerShell ISE
This section provides instructions on how to perform basic SNMP GET queries from a Windows environment using PowerShell
ISE and the snmpget command-line utility from the Net-SNMP suite. This method
is useful for querying specific OIDs from an anynode instance to retrieve configuration values, version numbers, or operational
status.
Prerequisites
Before running SNMP queries, ensure the following:
-
The Net-SNMP tools are installed on your Windows system.
You can download them from https://www.net-snmp.org.
-
The SNMP service is enabled and properly configured on the anynodesystem. Refer to the chapter Install SNMP on Windows
-
You know the community string (
public) and the OID you want to query. -
The PowerShell ISE is started with appropriate permissions.
Example Command
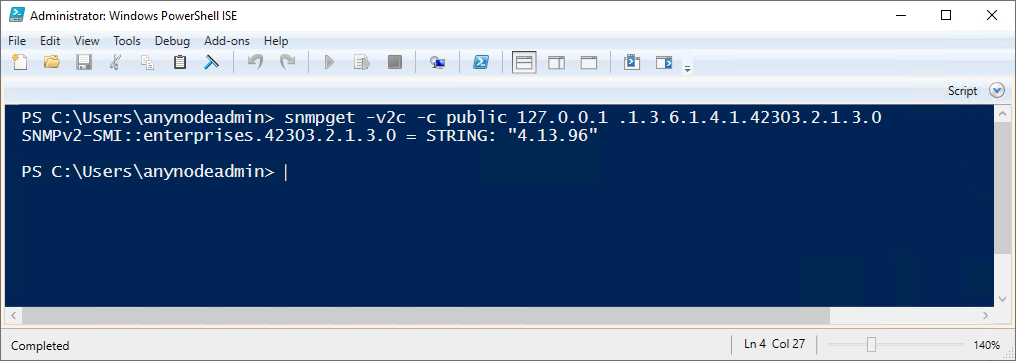
snmpget -v2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.4.1.42303.2.1.3.0
Explanation of Parameters
snmpget
The command to send an SNMP GET request.
-v2c
Specifies SNMP version 2c.
-c public
Community string used for SNMP authentication. In most default setups, "public" is used for read access.
127.0.0.1
IP address of the SNMP agent. In this example, it queries the local host (i.e., the same machine).
.1.3.6.1.4.1.42303.2.1.3.0
The object identifier (OID) refers to a specific value within the MIB tree. In this example, the anynode version number.
Sample Output
SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.42303.2.1.3.0 = STRING: "4.13.96"
This output indicates that the OID queried corresponds to a string value: "4.13.96".
In the context of anynode, this likely represents the currently installed software version.