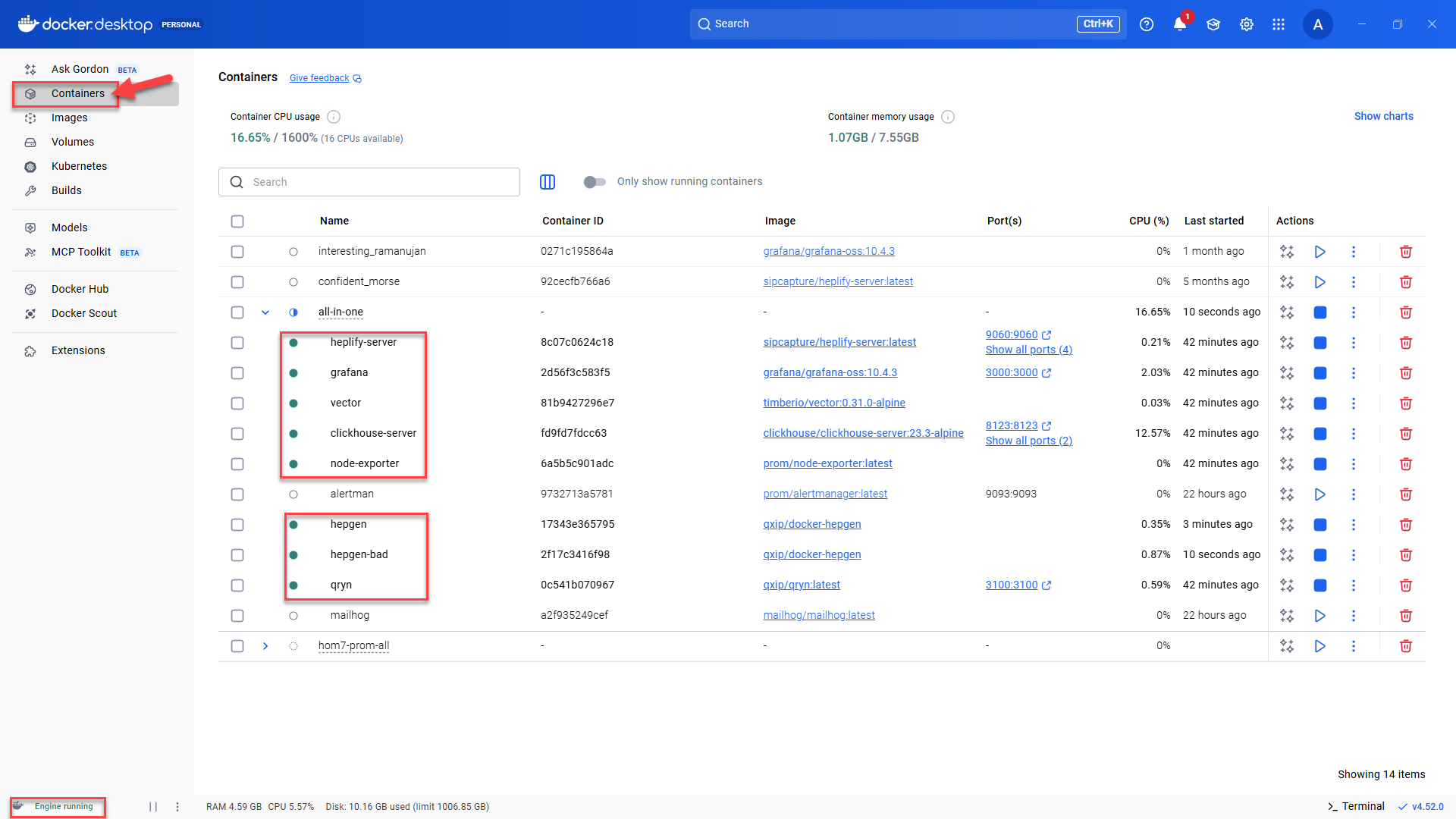
Start Homer 10 via Docker Compose
In PowerShell cd C:\homer-docker\all-in-one docker compose pull docker compose up -d
This downloads and starts
1. heplify-server
-
Receives HEPv3 packets from anynode
-
Listens on ports such as 9060/UDP or 9061/TCP
-
Decodes SIP/RTCP/log data
-
Forwards everything into qryn
2. qryn + ClickHouse
-
qryn acts as an observability backend
-
Exposes Prometheus-compatible and Loki-compatible APIs
-
-
ClickHouse stores the SIP/HEP capture data efficiently in a fast columnar database
-
Together they provide metrics, logs, and traces for Grafana without needing Prometheus
3. grafana
-
Connects directly to qryn (via its Prometheus or Loki API)
-
Dashboards for SIP/HEP data, system metrics, and analytics are preprovisioned in the all-in-one setup
-
Nothing else needs to be installed

Each container has a clear role
-
heplify-server = capture
-
qryn = ingest & index
-
clickhouse = storage
-
grafana = visualization
-
alertman + node-exporter = monitoring
-
vector = logs
-
hepgen + hepgen-bad = testing tools
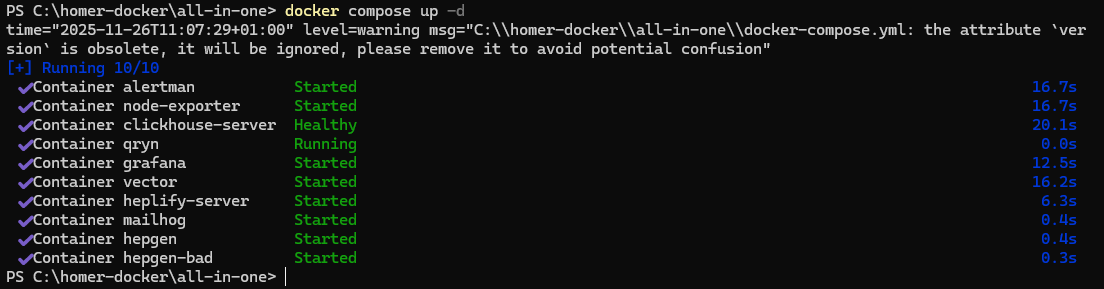
Verify all services are running in PowerShell
docker compose ps
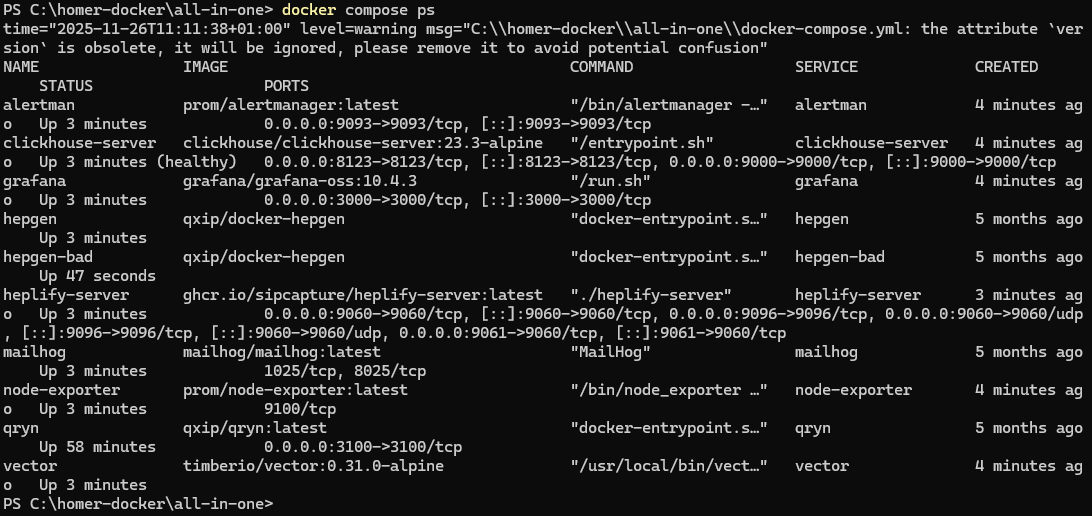

You can also check all running services in Docker Desktop on Windows, instead of using PowerShell. Docker Desktop provides a graphical interface where you can see the status of each container, view logs, restart services, or stop the entire stack with just a few clicks.
Start Docker Desktop.
Navigate to Containers in the left menu.
Check green status of the services.